Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) – Over the last eight years, there’s been a big buzz about CBDC. It has rapidly evolved in landscape of digital finance and has emerged as a significant innovation. It all started around 2014 when people began chatting and exploring the idea.
A big moment in the CBDC story happened when cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin came onto the scene. They showed that digital money could work without needing regular banks. This got central banks thinking: maybe digital money could be a game-changer, something to replace the cash we carry in our wallets. But it wasn’t until later that it really caught the attention of the financial world. In this blog post, you and I will delve into the intricacies of CBDC, examining its benefits, challenges, global developments, technological underpinnings, policy implications, and future outlook.
Designed and issued by central banks, CBDC represents a digital form of sovereign currency that holds the potential to reshape financial systems and empower economies worldwide. So, while the idea of CBDCs has been around for a while, it’s only recently that things have really started to pick up speed.
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) – Outlook
Central banks all around the world started diving deep into CBDC research. They were trying out new ideas, running test projects, and having lots of talks about how CBDCs could work. Then, in 2019 and 2020, things really started speeding up.
- CBDCs represent a transformative shift in the world of finance, offering the potential to revolutionize how we use and interact with money.
- As central banks worldwide continue to explore and experiment with CBDCs, their adoption and implementation are expected to accelerate in the coming years.
- CBDCs have the potential to foster financial inclusion, improve payment systems, and promote economic development by providing greater access to digital financial services.
- However, challenges such as privacy concerns, regulatory frameworks, and technological infrastructure must be addressed to ensure the successful integration of CBDCs into the global financial system.
Even big players like the People’s Bank of China (PBOC), the European Central Bank (ECB), and the Federal Reserve got in on the action. This shows how much the financial world is changing and how important digital money is becoming.
Benefits of CBDCs
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) promises a myriad of benefits. Firstly, it fosters financial inclusion by providing individuals with access to formal financial services, especially in regions where traditional banking infrastructure is lacking.
- Financial Inclusion: It have the potential to enhance financial inclusion by providing individuals with access to formal financial services, especially in regions where traditional banking infrastructure is lacking.
- Efficient Payment Systems: CBDCs can improve the efficiency of payment systems by reducing transaction costs and settlement times, leading to faster and cheaper transactions.
- Innovation in Financial Technologies: It facilitate the integration of innovative financial technologies, paving the way for greater economic development and prosperity by fostering the adoption of digital financial services.
- Reduced Dependency on Cash: It offer an alternative to physical cash, reducing the dependency on traditional currency and promoting the transition to a cashless society, which can streamline transactions and reduce the risks associated with physical currency handling.
Additionally, CBDCs can enhance the efficiency of payment systems, reducing transaction costs and settlement times. Moreover, CBDCs facilitate the integration of innovative financial technologies, paving the way for greater economic development and prosperity.
Challenges and Concerns
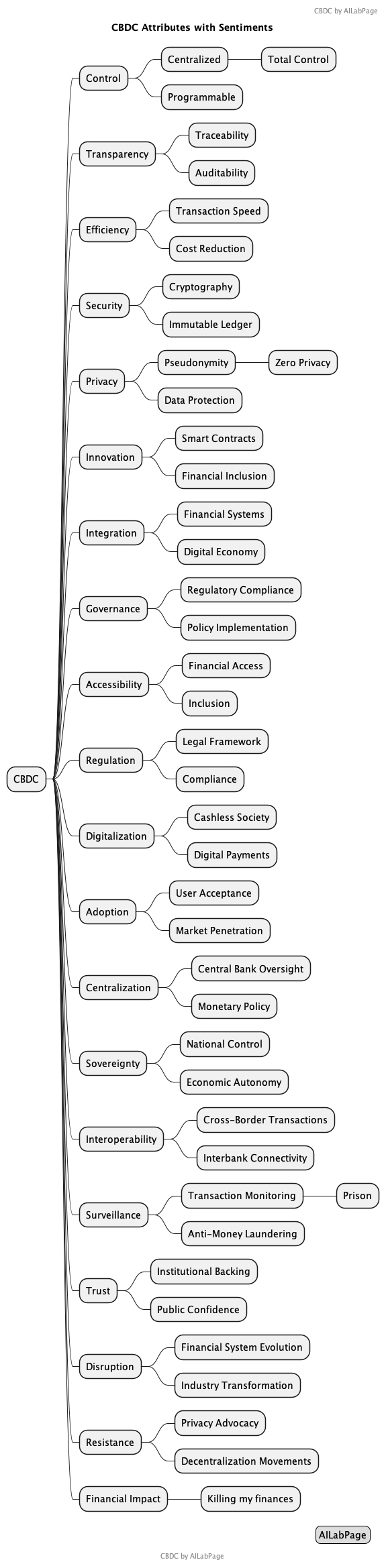
While CBDCs hold great promise, they also pose several challenges and concerns. Privacy emerges as a paramount issue, as the digitization of currency raises questions about data security and surveillance. The implications of CBDC and digital identification systems on individual freedoms and privacy. Let’s break down the key points raised
- Absolute Control: CBDCs will grant central banks significant control over financial transactions and potentially enable surveillance of individuals’ economic activities.
- Threats to Freedom: Critics argue that widespread adoption of CBDCs, especially when coupled with digital identification systems, could result in a ‘prison-like’ scenario, where individuals face the risk of absolute government control over their financial transactions. This could lead to a loss of privacy and autonomy, as every aspect of one’s financial life becomes subject to surveillance. Critics warn that such a system could restrict individual freedoms, ultimately undermining the fundamental principles of liberty and autonomy.
- Social Controls: Integration of CBDCs with digital identification could facilitate the imposition of social controls, potentially limiting participation in society based on arbitrary criteria set by government authorities.
- Programmable Currency: The programmable nature of CBDCs raises concerns about the potential for centralized authorities to impose restrictions on financial transactions based on factors such as compliance with regulations or political dissent.
- Unelected Oversight: Concerns are raised about the concentration of power in unelected officials’ hands, enabling them to make decisions that could affect individuals’ ability to participate in society without democratic accountability.
- Loss of Privacy: The integration of digital IDs and CBDCs could lead to a loss of privacy, as individuals’ financial transactions and personal information could be subject to monitoring and control by government authorities.
- Resistance: Calls for resistance against the imposition of CBDCs and digital identification systems emphasize the importance of preserving individual freedoms and the role of cash as a form of currency that enables financial transactions without government surveillance.
Furthermore, CBDCs could potentially disrupt the role of commercial banks and pose risks to financial stability if not carefully regulated. Addressing these challenges requires robust regulatory frameworks and safeguards to mitigate potential risks and protect users’ rights. Broader debates surrounding the potential risks and benefits of CBDCs and digital identification systems, highlighting concerns about their impact on individual freedoms, privacy, and democratic governance. They underscore the importance of careful consideration and public debate regarding the implementation of such technologies to ensure they align with principles of freedom, democracy, and human rights.
Global Developments
Around the globe, central banks are actively exploring CBDC initiatives. From pilot projects to comprehensive research efforts, countries are at various stages of CBDC development. Some nations are leading the charge with ambitious plans for CBDC implementation, while others are taking a cautious approach, weighing the implications carefully.
- Pilot Projects and Research Efforts: Central banks worldwide are conducting pilot projects and extensive research to explore the feasibility and implications of CBDCs, aiming to understand their potential impact on financial systems and economies.
- Diverse Approaches by Central Banks: Different countries and central banks are adopting diverse approaches to CBDC development, ranging from cautious exploration to ambitious implementation plans. This diversity reflects the complex and evolving nature of CBDC initiatives on a global scale.
- Collaborative Initiatives and Knowledge Sharing: International organizations, such as the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF), are fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing among central banks to facilitate the development and implementation of CBDCs. This collaborative effort aims to leverage collective expertise and insights to address common challenges and promote best practices in CBDC adoption.
The diversity of approaches underscores the complexity of the CBDC landscape and the need for collaboration and knowledge-sharing among policymakers.
Technology and Infrastructure
The underlying technology of CBDCs, such as blockchain or distributed ledger technology (DLT), plays a crucial role in shaping their functionality and security. Robust infrastructure is essential for ensuring scalability, resilience, and interoperability within financial systems.
- Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT): CBDCs often leverage blockchain or distributed ledger technology (DLT) for secure and transparent transactions. These technologies enable decentralized consensus mechanisms and smart contracts, enhancing the integrity and automation of transactions. AI algorithms can also be integrated to analyze transaction patterns for fraud detection and risk management.
- Digital Wallets and Mobile Applications: CBDCs are accessed through digital wallets or mobile applications, providing convenient and user-friendly interfaces for managing digital currency. These applications can utilize AI-powered personalization to offer tailored financial services and recommendations to users based on their transaction history and preferences.
- Scalable Infrastructure: Central banks require scalable infrastructure to support the widespread adoption of CBDCs. Cloud computing platforms and AI-driven automation can optimize infrastructure scalability and resource allocation, ensuring efficient processing of large transaction volumes. Neural networks can also be employed for predictive analytics to forecast demand and optimize resource allocation.
- Interoperability with Existing Systems: CBDC infrastructure must seamlessly integrate with existing payment systems and fintech infrastructure to facilitate interoperability and accessibility. APIs and open banking standards enable seamless integration with third-party financial services and applications, fostering innovation and expanding the CBDC ecosystem.
- Security Measures and Privacy Protocols: CBDC infrastructure incorporates advanced security measures and privacy protocols to protect user funds and data privacy. AI-powered cybersecurity solutions can detect and respond to cyber threats in real-time, enhancing the resilience of CBDC networks. Neural networks can also be utilized for anomaly detection and behavioral biometrics to identify suspicious activities and prevent fraudulent transactions.
Central banks must navigate technological challenges to build robust CBDC platforms capable of meeting the demands of modern digital economies.
Policy Implications
CBDCs have far-reaching policy implications, spanning monetary policy, financial regulation, and economic governance. Central banks must carefully consider their role in managing CBDCs, balancing the need for monetary stability with innovation and financial inclusion. Moreover, regulatory frameworks must evolve to address the unique characteristics of CBDCs, ensuring transparency, accountability, and consumer protection.
Future Outlook
As CBDCs continue to gain momentum, their future outlook remains dynamic and uncertain. Adoption trends, regulatory developments, and technological innovations will shape the trajectory of CBDCs in the years to come. The integration of CBDCs into the global financial system holds profound implications for individuals, businesses, and society as a whole. By navigating opportunities and challenges thoughtfully, central banks can unlock the transformative potential of CBDCs and foster inclusive, resilient, and sustainable financial ecosystems.

Conclusion – Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) represents a paradigm shift in the world of finance, offering new opportunities and challenges for policymakers, businesses, and consumers alike. As central banks navigate the complexities of CBDC implementation, they must prioritize transparency, accountability, and user-centric design to realize the full potential of this transformative technology. By fostering collaboration and innovation, CBDCs have the power to drive economic growth, promote financial inclusion, and shape the future of global finance in the digital age.
—
Points to Note:
it’s time to figure out when to use which tech—a tricky decision that can really only be tackled with a combination of experience and the type of problem in hand. So if you think you’ve got the right answer, take a bow and collect your credits! And don’t worry if you don’t get it right.
Feedback & Further Questions
Besides life lessons, I do write-ups on technology, which is my profession. Do you have any burning questions about big data, AI and ML, blockchain, and FinTech, or any questions about the basics of theoretical physics, which is my passion, or about photography or Fujifilm (SLRs or lenses)? which is my avocation. Please feel free to ask your question either by leaving a comment or by sending me an email. I will do my best to quench your curiosity.
Books & Other Material referred
- AILabPage (group of self-taught engineers/learners) members’ hands-on field work is being written here.
- Referred online materiel, live conferences and books (if available)
============================ About the Author =======================
Read about Author at : About Me
Thank you all, for spending your time reading this post. Please share your opinion / comments / critics / agreements or disagreement. Remark for more details about posts, subjects and relevance please read the disclaimer.
FacebookPage ContactMe Twitter ========================================================================

